Avoid Getting Leaky Gut
Gut health and avoiding a leaky gut is not only important for those of us with digestive issues but is important for all of us! The continuity and strength of our gastrointestinal (GI) membrane barrier is vital for immunologic functioning. The layered GI barrier system also permits our gut lumen spaces to hold and nurture essential gut bacteria. The intestinal barrier furthermore has the important job of keeping pathogens or microbes from freely accessing extra-lumenal abdominal organs or crossing into general systemic circulation.
It is instructive to contemplate this question:
What happens when the gut barrier is breached? [Hint: think about other barriers, such as a water dam barrier]

Just as water floods through a broken dam, particles flood through a broken Gastro-Intestinal Epithelial Barrier:
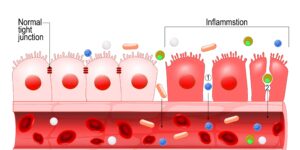
Damage to the intestinal epithelial barrier equates to an increase in gut permeability, which ushers a flood of undigested food particles and inflammatory mediators into the peritoneal cavity. After leaking to peritoneum, a cytokine storm (net: massive increase in immune system proteins) would then set the occasion for inflammation of pancreas, liver, gall bladder, and colon. Note also that this intestinal barrier breach could bathe this person’s gut tissues with infectious microbes. After microorganisms and undigested food products flood through the abdominal spaces, the blood and lymph fluids containing this ‘inflammatory mix’ could eventually circulate through the entire body. This is not a recipe for good health! Please visit the Natural Medicine Center and let our practitioners check your gut function (virtual appointments available too). Leaky gut leads ultimately to chronic inflammation, altered immune responses, allergies, and a low immune system responsivity [1].
Avoid getting leaky gut
- Do you have allergies or sensitivities?
Food allergies, but also other forms of food sensitivity, are best tagged as individualistic adverse food reactions. It is appropriate to call food intolerance symptoms ‘individualistic’ because each food-triggered-illness (e.g., peanut allergy) is likely to affect only a small segment of our population. Let’s say, in a family of four, Mom tests for a sensitivity to garlic. Dad’s GI tract, in constrast, tests to show lobster sensitivities. Perhaps the family panel of food testing shows that both children are intolerant if fed either egg whites or egg yolks. Food intolerances are that specific; which means that the plated food we serve in each household should be individualized. NMC is encouraging prevention and longevity by offering family discounts of $25.00 (2 or more tests)
To facilitate the readers’ understanding of this concept, let us contemplate the differences between gluten allergies and gluten sensitivities. Fact: only 1 percent of the world’s population has an IgE-mediated `formal` allergy to gluten—celiac patients, per the CDC and World Health Organization, fit this description. Counter Fact: up to 6 % of the world population suffers from a Nonceliac gluten sensitivity syndrome; the latter syndrome is a non IgE-mediated gluten sensitivity problem [2, 3]. Nonceliac gluten sensitivity is diagnosed in individuals who do not have celiac disease but who have intestinal symptoms, extraintestinal symptoms, or both, related to ingestion of gluten-containing grains, with symptomatic improvement when such grains are withdrawn from their diet.
The bullet points below list many common symptoms of a food sensitivity:
- Acne
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Constipation
- Dermatitis
- Diarrhea
- Eczema
- Fatigue
- GERD <a reflux disorder>
- Hives
- IBS
- Migraines
- Nausea
- Sinusitis
- Stuffy Nose
To prevent abdominal organ inflammation, our Doctors recommend abstinence from foods that provoke individualistic reaction patterns. We can help you discern your food sensitivity patterns; please call us for more details.
Prebiotics and Probiotics for Gut Health
Prebiotics are dietary fibers that serve the healthy bacteria in your digestive tract. Prebiotics aid in the digestion of our food and help us absorb more nutrients.
Probiotics help repair leaky gut by balancing the good bacteria in our digestive tract. Supplementing with probiotics has been linked to many health improvements including: mental health conditions, heart health, reducing allergies, reducing digestive disorders and improving overall immunity [4].
*Taking pre and probiotics is particularly important after being exposed to toxins, stress or after taking an antibiotic.
______________________________
Work Cited:
1. Fasano A. “All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases” (2020) doi:10.12688/f1000research.20510.1
2. Leonard M. “Genetics and celiac disease: the importance of Screening” (2015) Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9(2):209-15
3. Catassi C. ”The overlapping area of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity and Wheat-Sensitive Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Update” (2017) Nutrients 9, 1268
4. Sreeja V. “Probiotic Formulations: Application and Status as Pharmaceuticals—A Review“ (2013) Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins 5: 81-91

