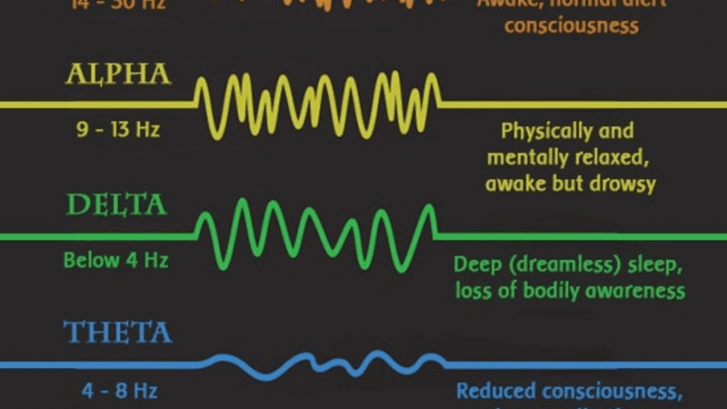
Before going further into Neurofeedback, it’s important to know exactly what this therapy is trying to change. Neurofeedback’s ability to improve cognitive performance and help treat various psychological disorders is based on a “re-training” of your brain to have more balanced and well regulated brain waves. Brain waves are the result of the electrical activity in your brain that creates your thoughts and operates your body. Neurologists have identified four different types of brain waves with unique properties based on their frequency range. A brief breakdown of the different brain waves can be seen below.

As you can see, brain wave activity can be divided into Beta, Alpha, Delta, Theta, and Gamma based on their frequency measured in Hertz.
Beta – 14-30 Hz
Beta waves are the most present brain wave during normal day to day activities. Beta is associated with alertness and focus which allows us to think critically and focus on school or work tasks. An overabundance of beta waves are typically linked to people with high stress or anxiety and low amounts of beta waves are usually seen as a contributing factor to ADHD/ADD and depression.
Alpha – 9-13 Hz
Alpha waves come from a relaxed state of mind, especially after doing a difficult or stressful task that required heavy beta waves. Alpha waves are also important when getting into the deep sleep states of delta and theta thus insomniacs are generally found to have low levels of alpha activity. People who are chronically stressed or anxious also generally have too low alpha waves while those who are seemingly never stressed or take anything seriously have excessive alpha activity making them overly relaxed.
Delta – Below 4 Hz
Delta waves are the slowest type of brain waves and is generated in both deep dreamless sleep and focused meditation. These waves have been shown to be important in the healing process of the body and are one reason why healthy sleep is necessary for healing or recovery. Excessive or irregular delta waves, especially while awake, are usually telling of either Traumatic Brain Injury or a learning disability.
Theta – 4-8 Hz
Theta waves are the link between alpha and delta and are mainly found in daydreaming or sleep, but can also be achieved through deep meditation or relaxation techniques. Theta waves are associated with unconscious memories and emotions which often arise in dreams. Theta waves have also been shown to help spark people’s creativity and imagination. While theta waves are very beneficial for the body, too much theta activity can lead to ADHD and depression while too little theta activity can cause anxiety, stress, and poor emotional responses.
Gamma – 30 Hz and above
Gamma waves are the fastest known brain waves in our body and are mainly involved in higher order cognitive functions and information processing including sensory information. While they are not as common or well studied as other brain waves, they are believed to be an important part of learning and low gamma wave activity is often seen in people with ADHD or learning disabilities.
Brainwave Regulation
Now that you have an idea of what the different brain waves are and how they affect the way you think, I hope you can see the importance of having a well regulated and balanced brain. While these different brain waves and states can’t be immediately shifted, there are many ways a person can learn to regulate their brain activity for optimal performance. When you drink a coffee, your helping your brain boost its level of beta waves for increased focus and productivity; on the other hand, relaxation or meditation techniques can lower beta activity and raise alpha causing a more relaxed alpha state. While nearly all illicit or prescription drugs have effects that help enhance or inhibit certain types of brain activity, healthy brain regulation can be achieved naturally through neurofeedback training.
More often than not, medication such as anti-depressants or stimulants are prescribed to fix brain imbalances. While medication can improve functioning and brain balance, they also come with side effects and drawbacks such as dependence and tolerance. Instead of using prescription drugs to fix imbalances in brain wave activity, neurofeedback therapy relies on proven QEEG technology to train the brain to better regulate itself. By using audio and visual cues neurofeedback training programs inform your brain when deviant or abnormal activity arises allowing your brain to make proper adjustments. While much of the “learning” process is unconscious, neurofeedback trains your brain to stay in states of optimal functioning and avoid the imbalance errors it would previously make.
Neurofeedback Changing Brain Waves
In addition to the many studies done showing subjective improvement of patients symptoms after neurofeedback training, a number of studies have demonstrated neurofeedback’s objective ability to significantly change underlying brain wave activity. One such study measured their participants brain activity before and after 6 sessions of neurofeedback training in comparison to a control group and showed a significant change in brain wave activity in the neurofeedback group. The graph below demonstrates the significant changes in brain wave activity that neurofeedback training caused in comparison to a normal non-trained group as based on a study done in 2016. (Oh, Hyun-Ju, Song, Gui-Bin 2016.)
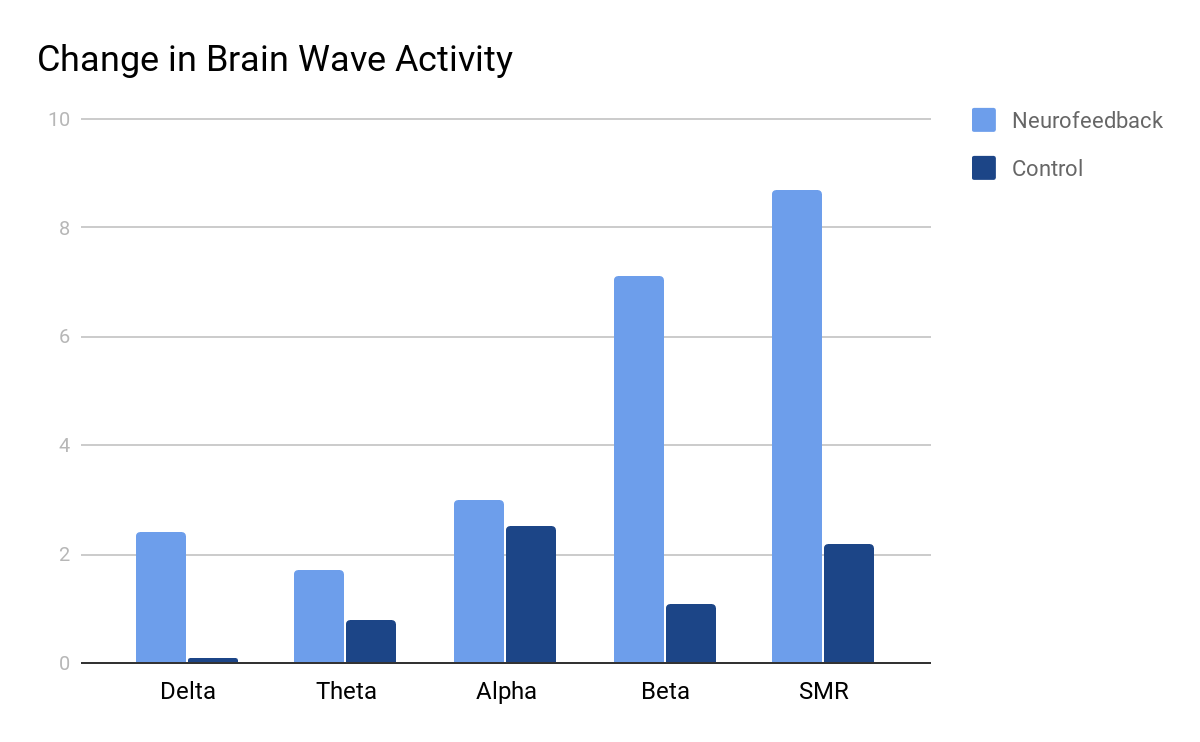
Oh H-J, Song G-B. Effects of neurofeedback training on the brain wave of adults with forward head posture. Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 2016;28(10):2938-2941. doi:10.1589/jpts.28.2938.